3D Artist Roadmap: Beginner to Professional
Want to become a professional 3D artist and master modeling, texturing, and animation? A career as a 3D artist combines creativity, technical skill, and consistent practice. Every stage, from modeling simple objects to producing high-quality, production-ready assets, is essential for building professional expertise.
For beginners, following a structured 3D artist roadmap can save time, reduce confusion, and accelerate skill growth. This step-by-step guide helps aspiring 3D artists gain the technical knowledge, practical experience, and workflow discipline needed for studio-level projects.
Following this path can turn raw potential into a polished skill set that meets industry standards.
What Does a 3D Artist Do?
A 3D artist creates digital objects, characters, and environments using three-dimensional software. These assets are used in films, games, advertisements, product visualization, and architectural projects. The responsibilities of a 3D artist vary depending on the industry and specialization, but the core goal remains the same: creating accurate, visually appealing 3D assets that meet project requirements.
Most professionals focus on a specific area such as modeling, texturing, animation, or lighting. This focused approach allows better skill growth and improves job readiness.


Beginner Stage: Learning the Basics
The beginner stage focuses on understanding core principles and becoming comfortable with basic tools. At this level, the aim is not perfection but clarity.
Before working on complex models, beginners must learn essential 3D concepts. These concepts apply across all software and help avoid mistakes later in the learning process. Important basics include polygon structure, mesh flow, object transformation, and scale.
Beginner Focus Areas:
- Understanding points, edges, and faces
- Basic object creation and editing
- Navigation and viewport controls
- Simple lighting and camera setup
Choosing Your First Software
Selecting one main software is important during this stage. Blender is popular for beginners due to its free access, while Autodesk Maya and 3ds Max are widely used in professional studios. Learning one tool properly builds confidence and avoids confusion.
Regular practice with simple objects such as furniture, tools, or everyday items helps develop accuracy and hand control.
Get to know: Best 3D Modeling Online Courses for Beginners
Choosing Your First Software
Selecting one main software is important during this stage. Blender is popular for beginners due to its free access, while Autodesk Maya and 3ds Max are widely used in professional studios. Learning one tool properly builds confidence and avoids confusion.
Regular practice with simple objects such as furniture, tools, or everyday items helps develop accuracy and hand control.
Get to know: Best 3D Modeling Online Courses for Beginners
Intermediate Stage: Improving Quality and Technique
Once basic modeling feels comfortable, artists can move to the intermediate level. This stage focuses on improving asset quality and learning production-related techniques.
Intermediate artists begin working with more detailed models and structured workflows. Clean topology, correct proportions, and organized scenes become important at this stage.
Instead of listing only tools, this stage should focus on applying skills through practice. Creating props, small environments, or basic characters helps bridge the gap between learning and production.
Skills to Develop at This Level:
- Hard-surface and organic modeling basics
- UV unwrapping and layout
- Texture painting and material setup
- Basic rendering and presentation
Texturing plays a major role in improving realism. Learning PBR workflows and understanding how materials react to light adds depth to 3D assets.
Tip: Following a structured 3D artist career path helps you develop essential skills step by step. Focus on learning current tools and techniques, and avoid relying on outdated software or irrelevant tips.
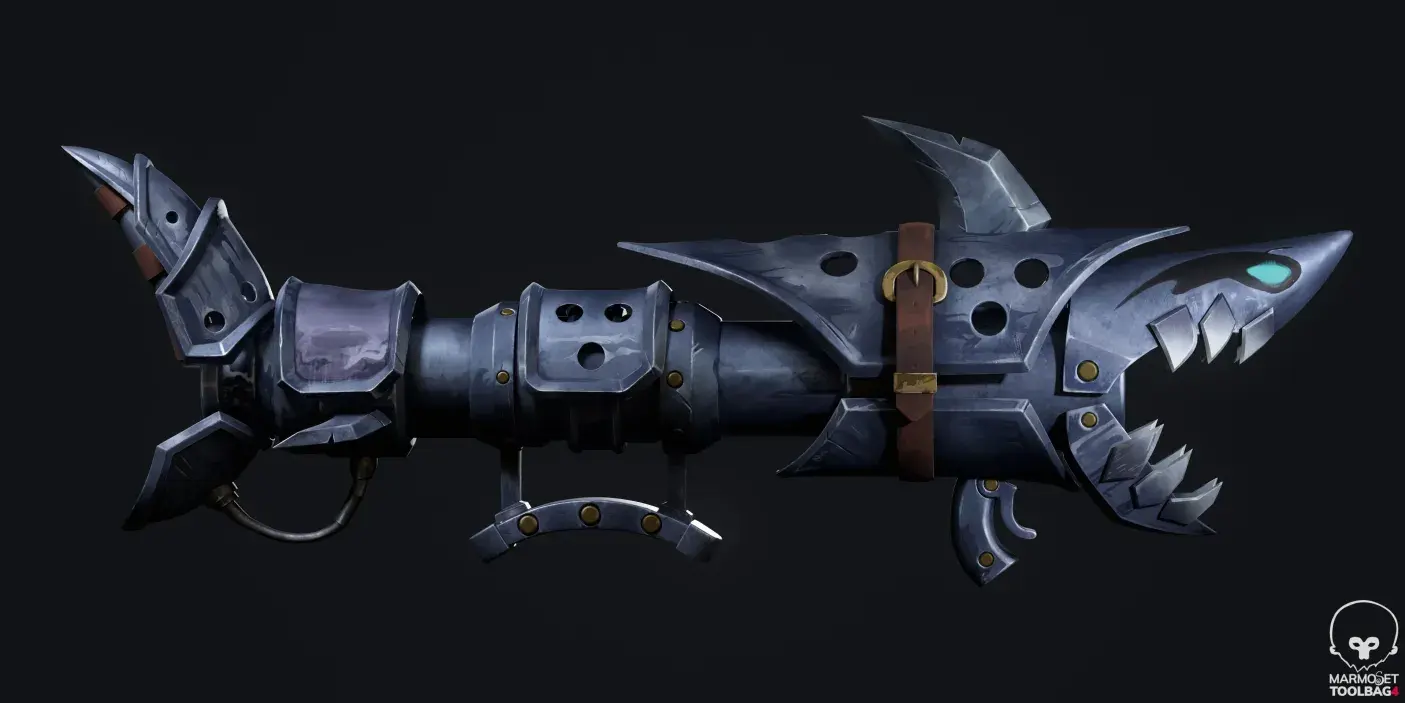

Lighting and Rendering Knowledge
Lighting and rendering define how a model appears in the final output. Even a well-modeled asset can look poor without proper lighting. Artists should learn how light direction, intensity, and color affect a scene.
Rendering engines such as Arnold, Cycles, or V-Ray are commonly used. Knowing how to set up clean renders improves portfolio presentation and client communication.
Choosing a Specialization
After reaching an intermediate level, artists should select a specialization. Trying to master everything often leads to slow progress and confusion.
Common specialization paths include character modeling, prop modeling, environment creation, animation, and lighting. Each path requires a different focus and workflow.
Popular 3D Artist Roles:
-
- 3D Modeler
-
- Animator
-
- Lighting Artist
Choosing a specialization helps artists align their learning with job requirements and industry demand.
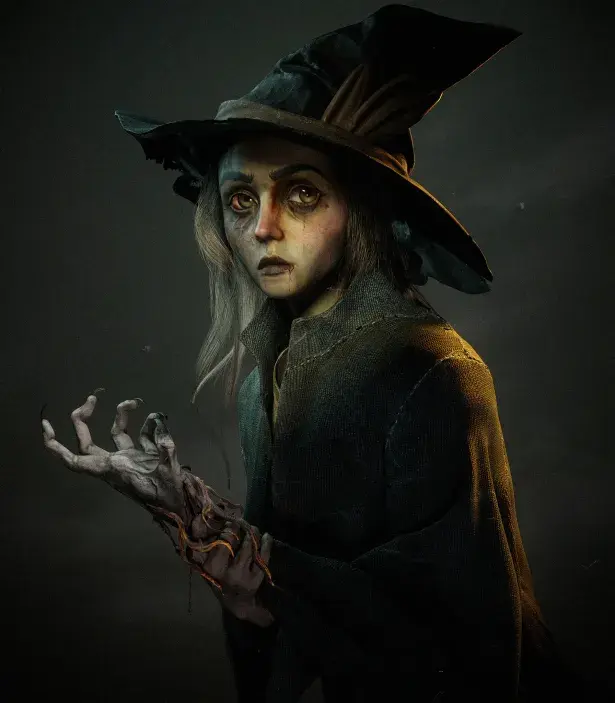


Advanced Stage: Professional Skill Development
The advanced stage focuses on production-quality output and efficiency. Artists at this level follow structured pipelines and work with accuracy and consistency.
Professional workflows include reference study, blocking, detailed modeling, clean UVs, texture baking, and final rendering. Understanding this process improves speed and reduces revisions.
At this stage, artists should prioritize quality over quantity. Fewer polished assets are more valuable than many unfinished ones.
Advanced Skills Include:
- Clean topology for animation or games
- Asset optimization
- High-quality texturing
- Scene organization and naming standards
Game artists should also learn basic engine integration and optimization techniques.
Final Stage – Professional Career Preparation
Building a Strong 3D Portfolio
A portfolio is the ultimate showcase of a 3D artist’s career. Studios and clients rely heavily on portfolio quality when hiring.
A strong portfolio should clearly show specialization. Each project should include final renders, wireframes, and texture details. A clear presentation makes it easier for reviewers to evaluate skills.
Portfolio Tips:
- Focus on 6–10 strong projects
- Show process and breakdowns
- Maintain consistent quality
- Use platforms like ArtStation or Behance
Personal projects often make portfolios stronger because they show creative thinking and commitment.

Gaining Industry Experience
Entry-level roles and internships help artists gain production exposure. Working with teams teaches deadlines, feedback handling, and pipeline discipline.
Junior positions allow artists to apply skills in real projects while continuing to learn from senior team members.
Learning should not stop after getting a job. Skill improvement, software updates, and artistic practice remain part of long-term career growth.

Importance of Soft Skills
Along with technical abilities, soft skills play a major role in professional success. Communication, time management, and adaptability help artists work effectively in team environments.
Being open to feedback and willing to improve leads to better collaboration and steady growth.
Related Articles:
3D Art vs Game Development: Which Career Path Is Right for You?
How to Master Maya’s Animation Tools
Choosing the Best Online 3D Animation School for Your Career


How Does M3DS Academy Help You Become a Professional 3D Artist?
Building a successful 3D career starts with the right guidance and structured training. M3DS Academy supports students at every stage of the 3D artist roadmap, from basic concepts to professional production skills. Our training begins with strong fundamentals in modeling, software navigation, and workflow clarity.
As learners progress, we focus on texturing, lighting, rendering, and structured asset creation aligned with studio practices. Our mentors guide students through hands-on projects that build confidence and technical accuracy. We also help students create focused portfolios that meet industry expectations.
Through consistent practice, feedback, and practical guidance, our programs prepare learners for real production environments.