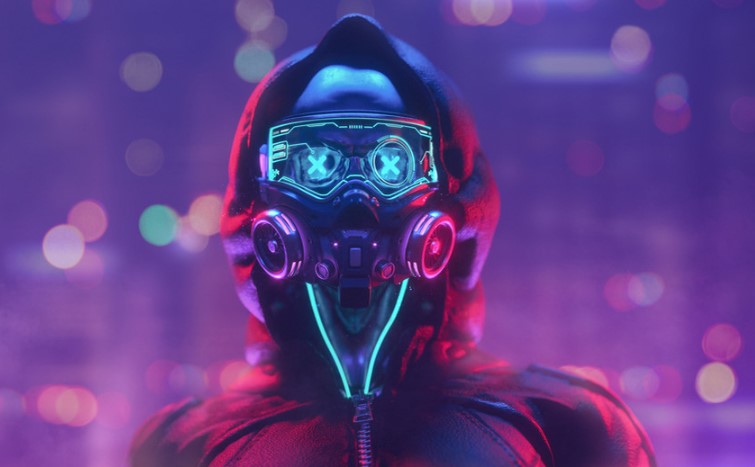
Texture Artist: Job Duties, Skills, Role & Responsibilities
Texture artists are incredible artists who create the textures of 3D models and work tirelessly to bring them to virtual worlds. They know skin properties in humans and animals, textiles, geographic elements, architectural finishes, landscapes, etc. With games now requiring more realistic finishes, the demand for the role of the Texture Artist is increasing.
What does a texture artist do?
Part of the work of the Texture Artist, in line with this trend, is to scan photographs and apply them to objects and environments created by the 3D modelers.
The creation of custom textures is based on realism, but they are to be used in fantasy worlds, objects, and creatures. Gameplay increases, and players get less bored when game worlds are filled with various surfaces. Modelers and shading/lighting technical directors work near the texture artist to develop the best elements in the game world.
Texture artists in live-action movies and 3D animation
Texture artists in live-action film and 3D animation usually provide the textures of the parts of projects that require complicated texturing. This would be more realistic in live-action films as it needs to match up with the video and sometimes give the appearance of a real-world surface.
The creation of original texture may be based on realistic production but will be for fantasy worlds, objects, and animals. Adding different surfaces within game worlds will encourage gameplay by making it varied for the player.
Texture artists work closely with modelers and shading/lighting technical directors who create video games to provide the best elements for the game world.
The texture artists of the live-action movies and 3D animation would render textures of parts of projects that need detailed texturing. In the case of live-action films, it will be more realistic since it has to integrate well with the video and, at times, simulate real-world surfaces.
Texture artist: Job description & Duties
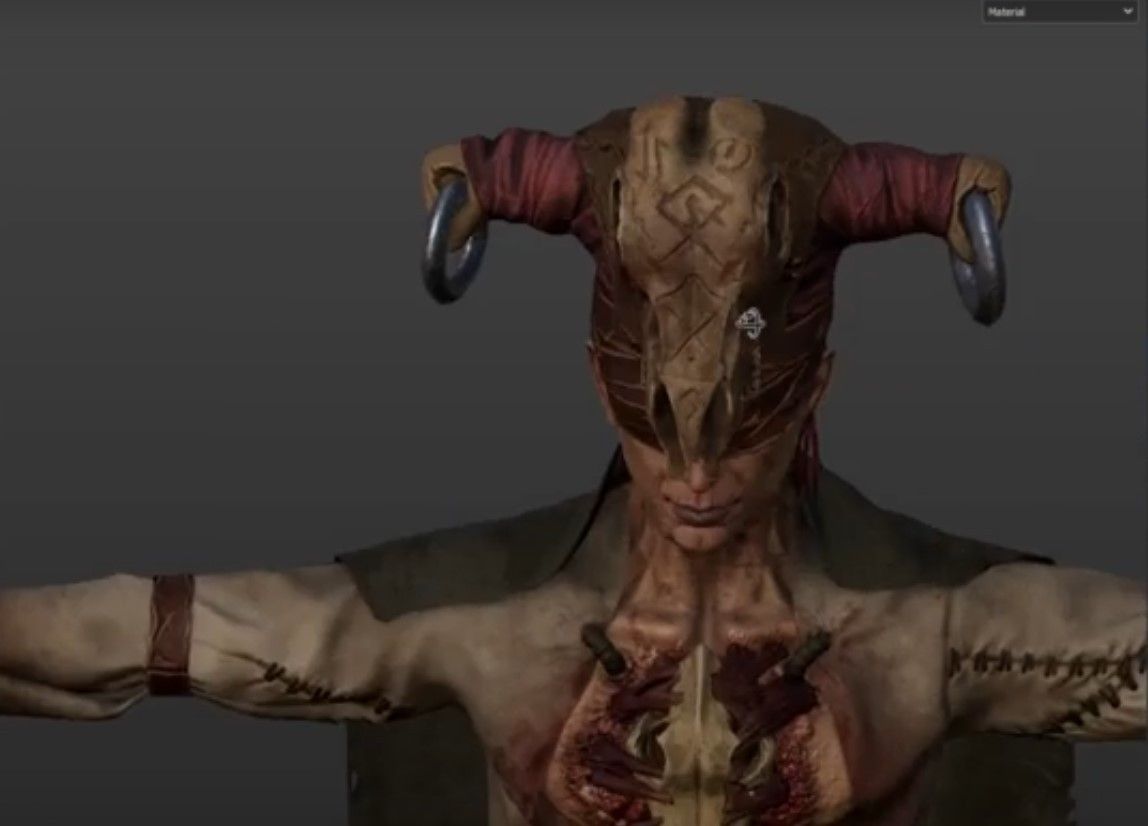
The role of a texture artist in the gaming industry is to create realistic or fantastical textures or surfaces that an object or character may have in a 3D computer model. This is a specialized field, taking thorough knowledge of surface qualities such as skin, flesh, fur, hair, scales, textiles, armor, metallic finishes, nails, claws, membranes, and various others.
The Texture Artist needs an in-depth understanding of the skeletal framework and rigging that underlies and drives the models. It has to be ensured that the texturing works as a layer on top of the moving parts. In this case, the Texture Artist should be able to make sure the texture layers are compatible with the motion of the model. He concludes that the job of a Texture Artist demands a range of skills, from texturing techniques to 3D modeling and animation for high-quality output.
Textures are created from scratch or real-world references using scans imported and shaped into graphical elements. As gaming graphics become more complex, the expected outcomes from a Texture Artist become ever more accurate and dynamic.
The work of the Texture Artist can go from live-action to animation, creating textures for 3D models during the production phase. The result in live-action projects will be realism, while the feel of animation projects requires a coherence of style.
Role & responsibilities of a texture artist in movies & games
- Communicating with designers and developers regarding the design brief
- Communicating with the Director/cinematographer and Design Department regarding the finishes of the texturing
- Reference gathering regarding aesthetics and genre of game, film, or animation
- Work with post-production and visual effects teams to ensure seamless integration with footage.
- Develop and refine textures throughout production.
- I am communicating with animators and modelers regarding the most suitable textures for each object and character.
- Create compellingly diverse and interactive textures that will engage the player and enrich the gameplay.
- UV mapping
- Ensure high-level design and photo realism throughout
- Curating the consistent look of all elements of the Game or Film
Skills required to become a texture artist
Every Texture Artist is always looking for textures in the real world to bring into their work. They need an eye for detail since all surrounding them could eventually be used as a reference point for surfaces or character skin.
Game and film studios can seek the following skills in a texture artist:
- Computer graphics, 3D animation, or graphic design training
- Background in texturing 3D models; knowledge of modeling rigs.
- Pull inspiration consistently from real-world references.
- Firm grasp of the visual language: dimension, scale, perspective, shade, texture, color, composition, depth of field, proportion, lighting, spatial awareness, etc.
- Foundational understanding of anatomy
What software and tools does a Texture Artist use?
Texture artists must comprehend their path around the software used by 3D modelers and have better texture-specific programs that they include in their work.
Texture artists may require knowledge of a mixture of the following software:
- Zbrush
- Substance Painter
- Maya
- Mudbox
- Adobe Photoshop
- Mari
Conclusion: Shaping the Visual Depth
Whether it’s skin, fur, metal, or other fabrics, texture artists specialize in creating detailed surfaces for 3D models, making virtual worlds very rich and variable.
However, what they do is not just splat some textures; they have to make sure these textures work in concert with the 3D models and animations beneath them.
As technology continues to improve, so does the demand for professional texture artists. With excellent knowledge of anatomy and materials combined with a deep understanding of visual storytelling, these artists are pushing every limit to what one can do with digital art, improving the experience of gameplay and cinematic realism with each passing day. They are vital to making virtual worlds feel realistic and interactive to audiences.
Gain all-encompassing skills with our academy programs, and browse our 3d art and game dev courses if you are more oriented toward a specific skill. Also, engage with industry experts through our masterclasses to gain valuable insights in the field.
Apply today and gamify your learning journey with the M3DS Academy teaching approach.