Unreal Engine Lighting: From Post-Processing to Camera Setup
🟡Recent industry reports reveal that 78% of video game developers and 65% of movie studios believe post-processing effects and lights are necessary for making top-notch visuals. This tutorial will give you everything you need from UE4’s built-in tools–all while showing off their power too!
🟡 We’ll start by copying over an example project so there are no unwanted light sources messing things up; we’ll also remove any default settings related to this. After doing so, It’ll be like starting completely fresh – just better because now we can do things right! Our focus next turns towards creating outdoor scene using Environmental Light Mixers (ELM). They’re good at handling lots of different types of light and combining their effects; meaning users have precise control with ease.
🟡 But That’s not all: As well covering standard topics such as focal length setting camera position correctly when taking pictures—it also goes through more advanced areas like adding special effects afterward. For instance, adjusting exposure levels so your image isn’t too dark or bright after applying filters that make colors look distorted along the edges of objects (Chromatic Aberration).
Workflow for Setting Up Environment Lighting in Unreal Engine
1. Prepare Your Project
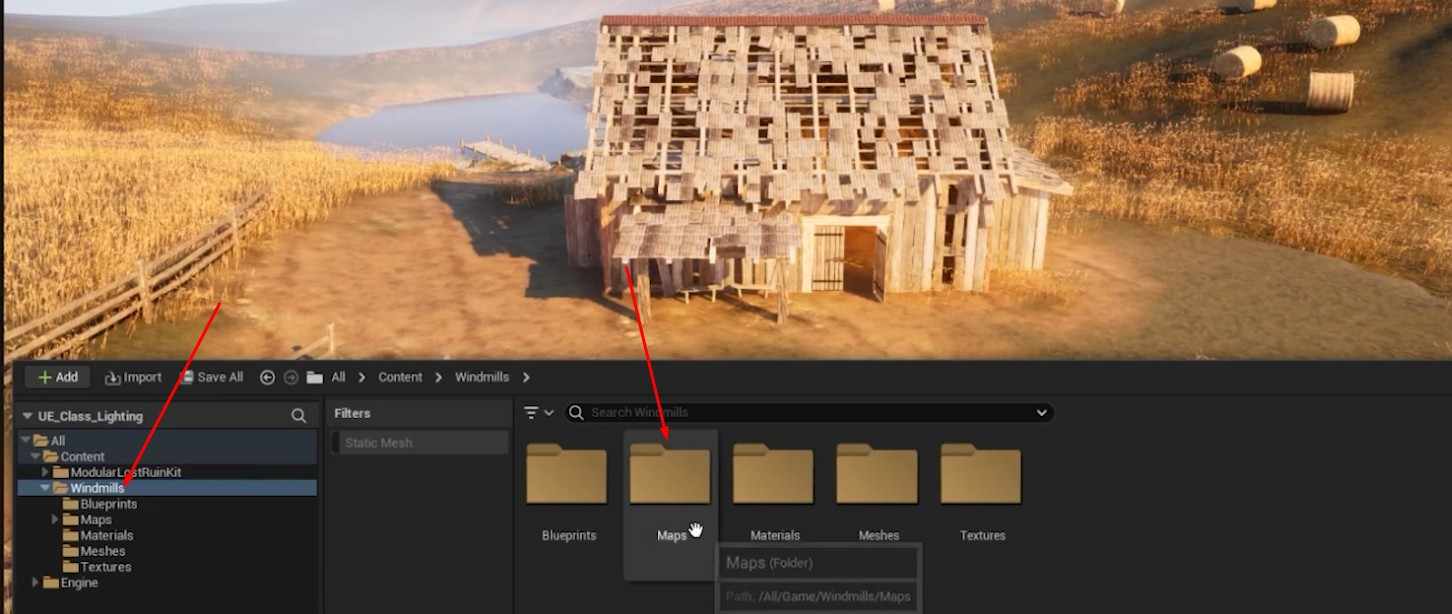
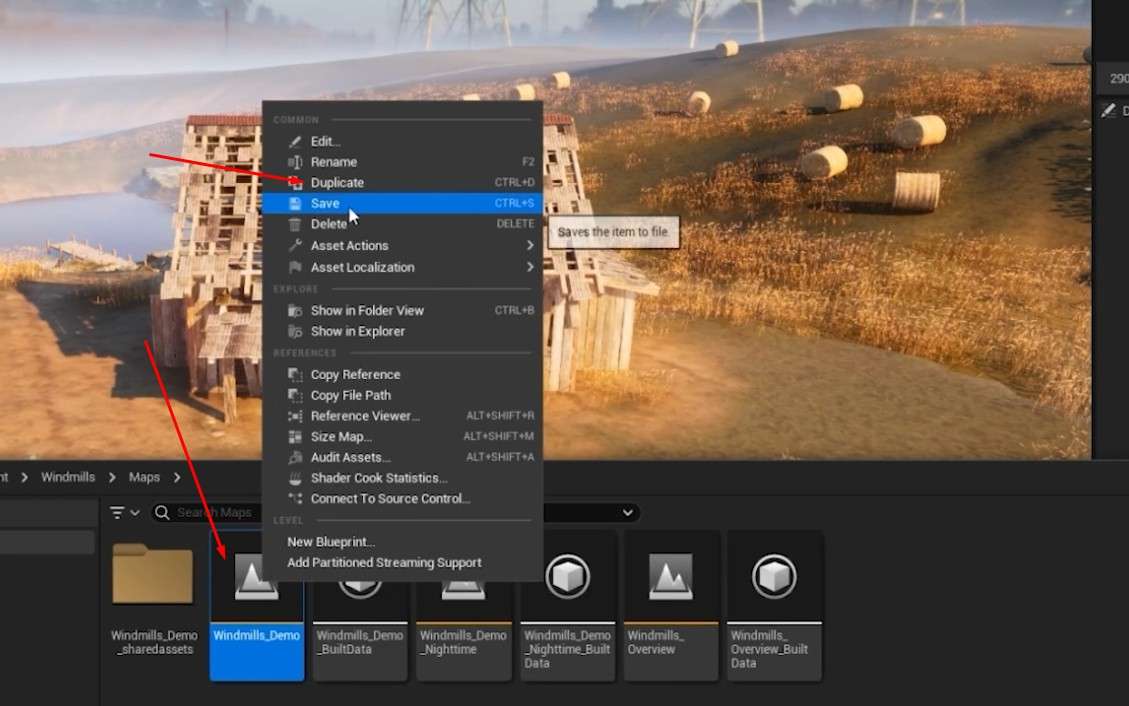
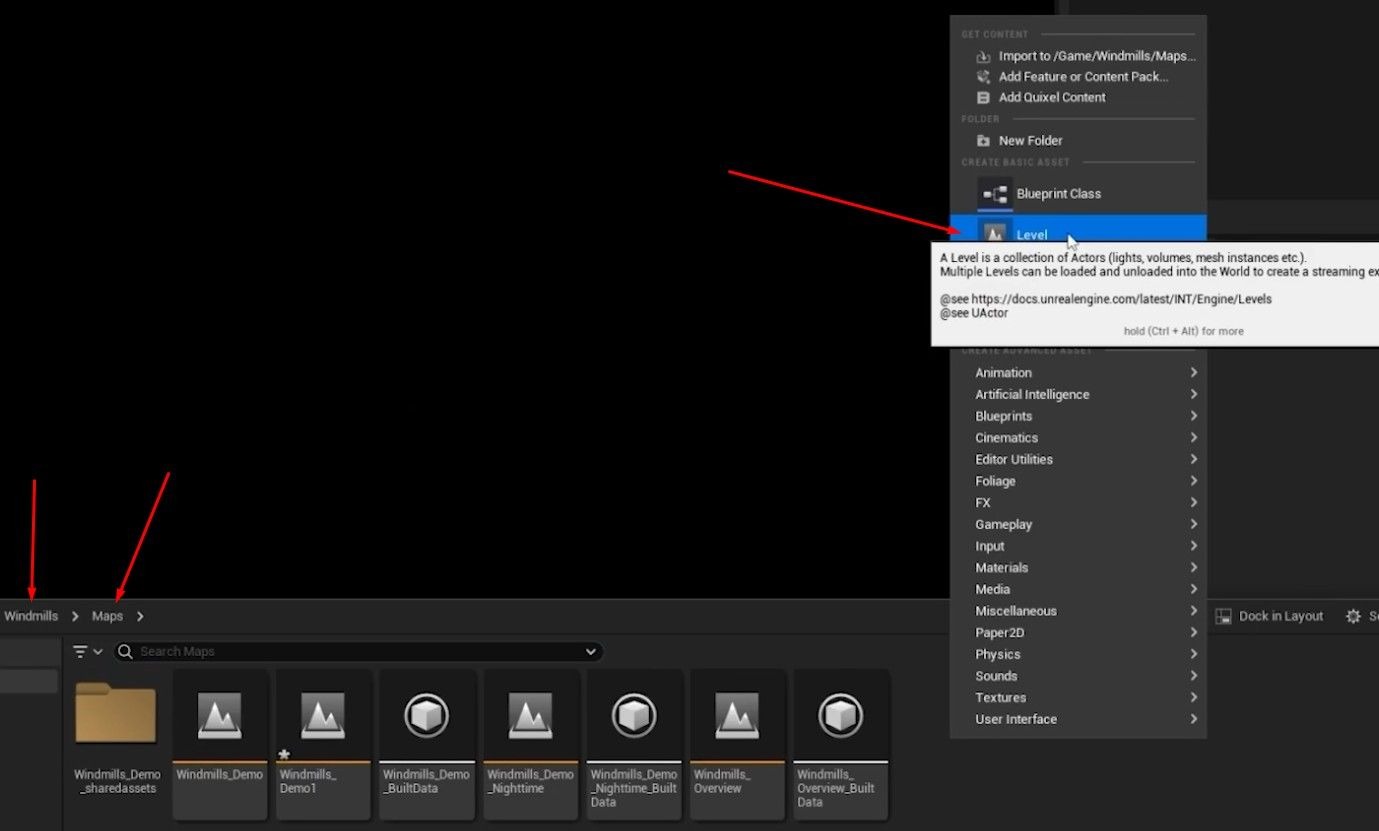
- Duplicate the Level: Start by duplicating the level found in the Maps folder of your Unreal Engine project.
Remove Existing Lights: Delete all current light sources in the level to begin with a clean slate.
2. Create and Set Up a New Level
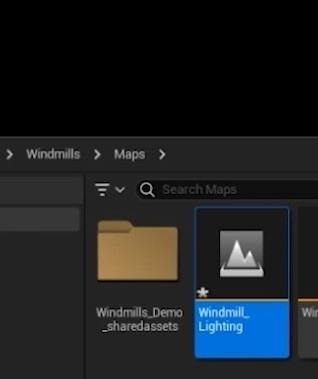
- Create New Level: Create a new level and name it Windmill_Lighting.
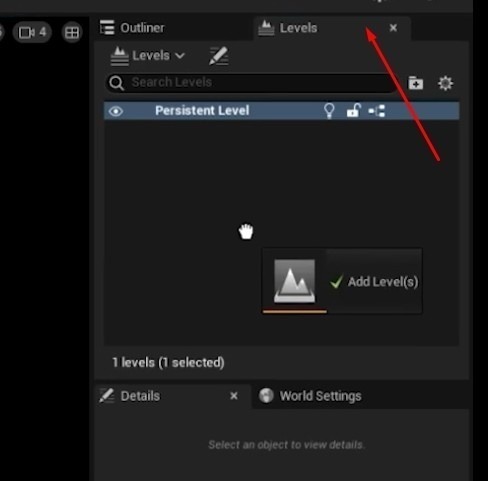
- Add to Levels Tab: Add the new level to the Levels tab within your workspace to keep everything organized.
3. Configure Environment Lighting
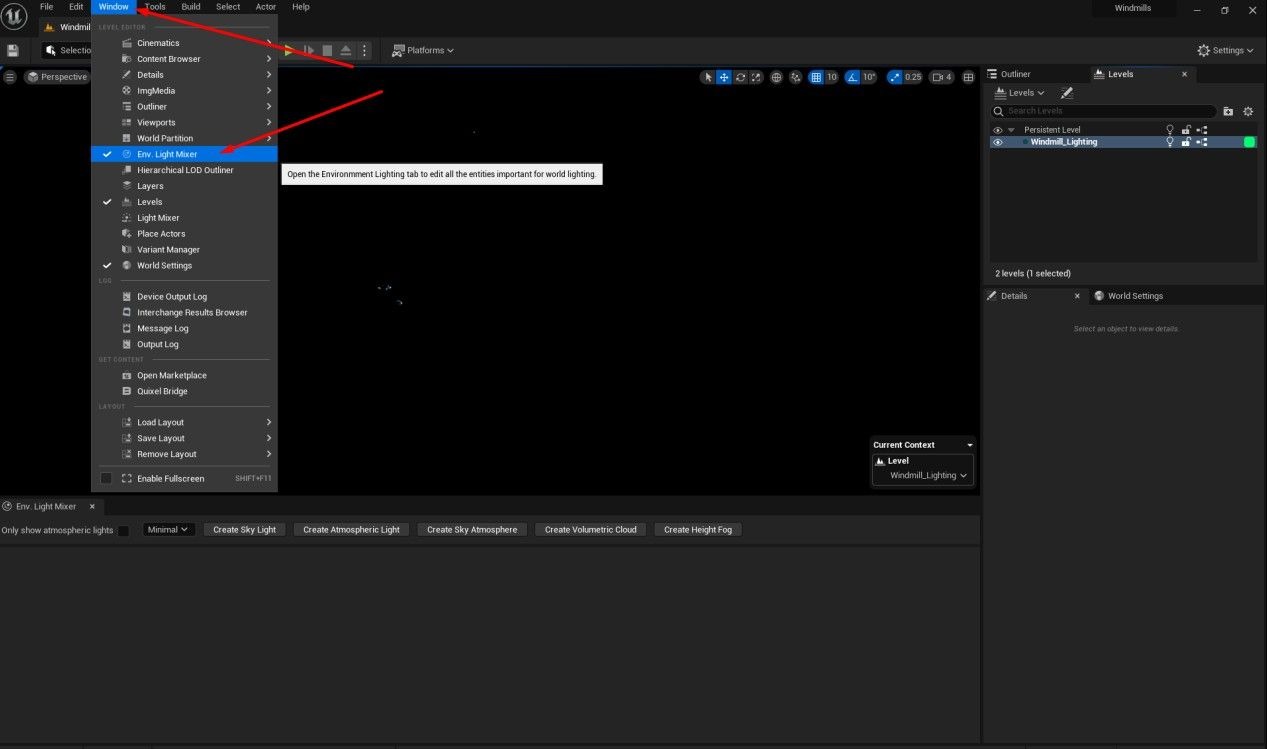
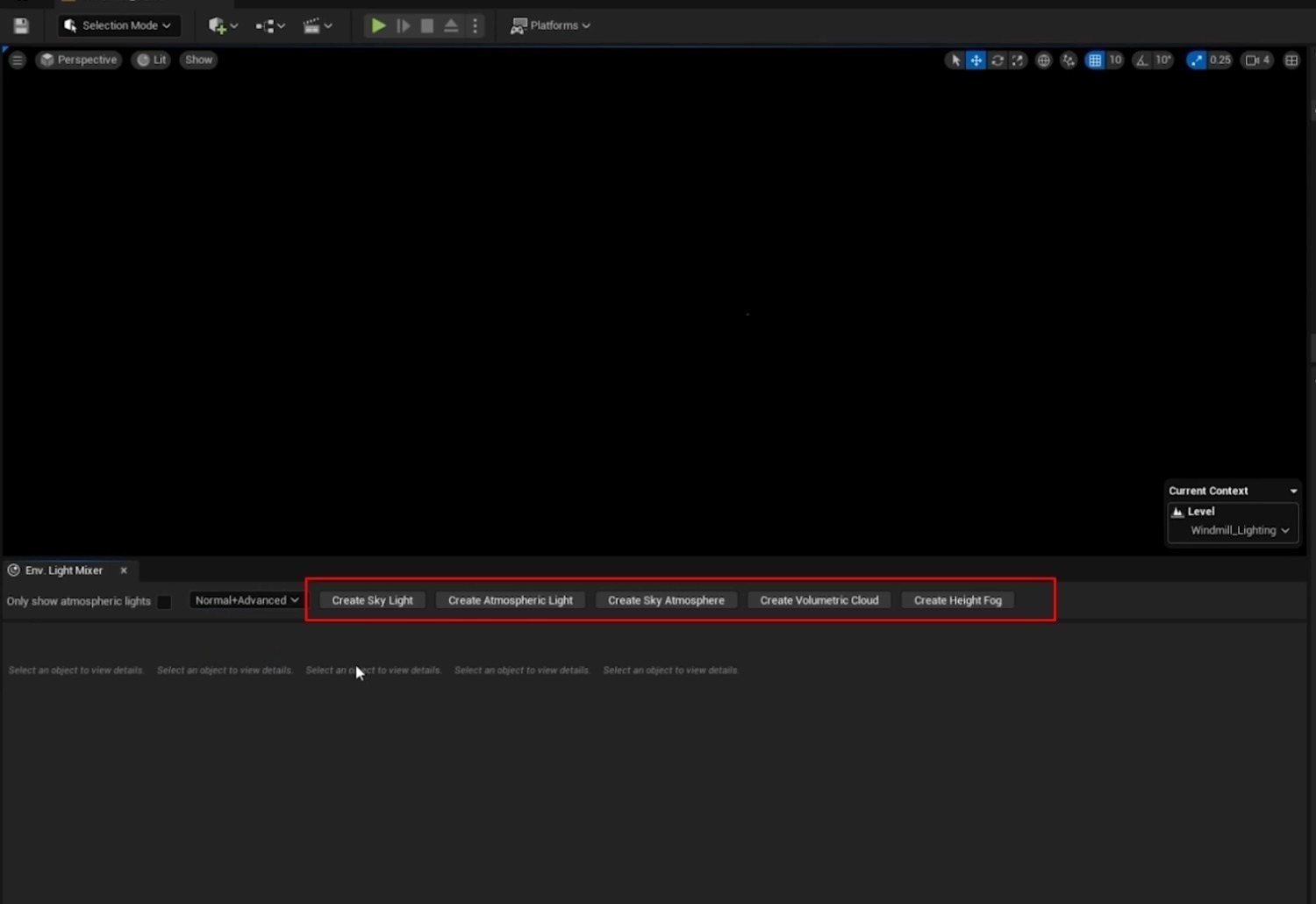
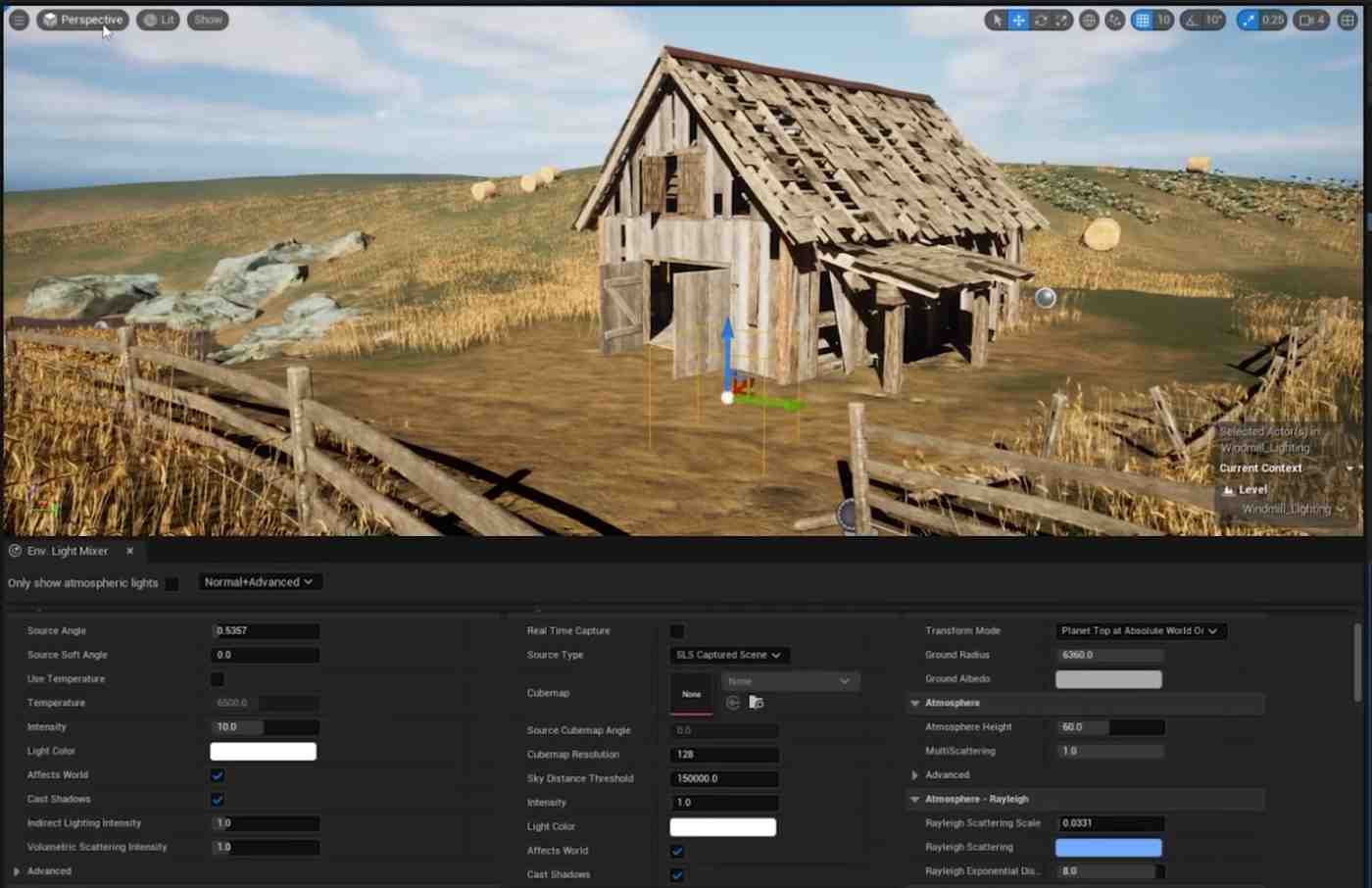
- Add Environment Light Mixer: Access the Windows tab, add the Environment Light Mixer to your workspace, and dock it for easy access.
Set Light Mixer Options: Set the Environment Light Mixer to Normal+Advanced and select all Create options to reintroduce environmental light
4. Adjust Post-Processing Settings
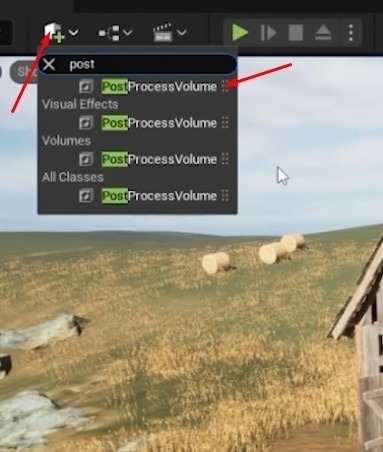
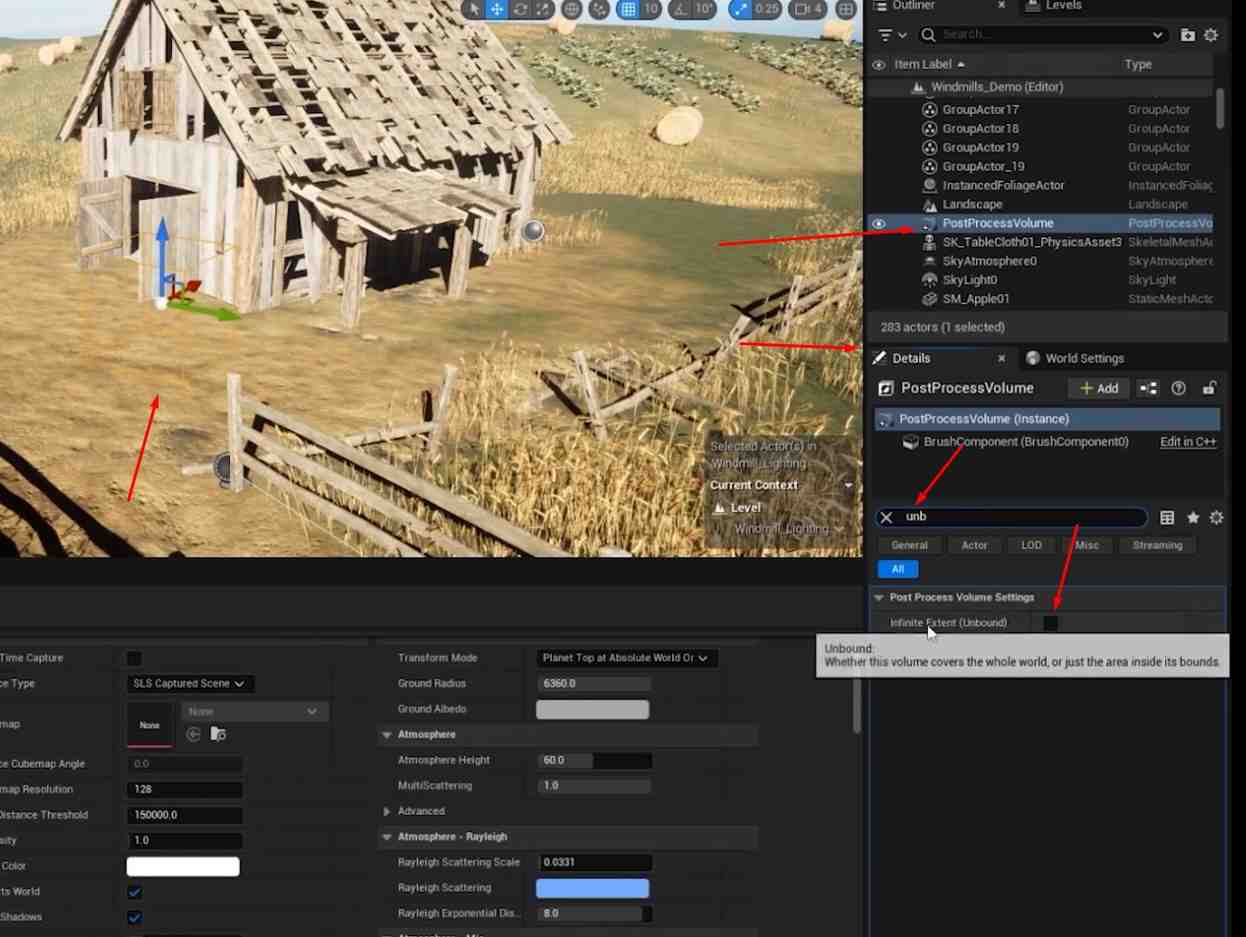
- Add PostProcessVolume: Insert a new PostProcessVolume into the scene.
- Enable Infinite Extend: In the Details panel, check the Infinite Extend box to apply post-processing effects across the entire scene.
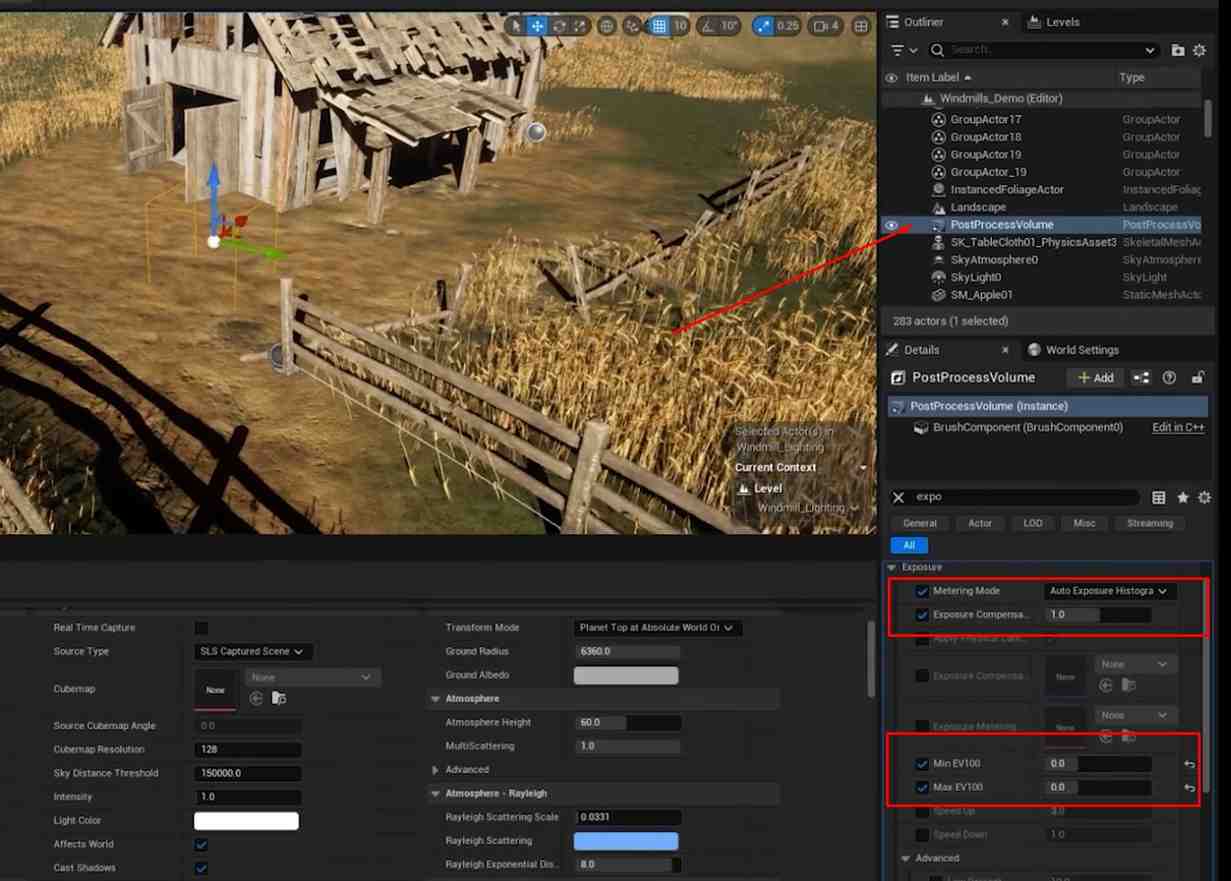
Configure Exposure Settings: Set Metering Mode, Exposure Compensation, Min EV100, and Max EV100 to 0 in the PostProcessVolume Details to standardize exposure.
5. Set Up the Cinematic Camera
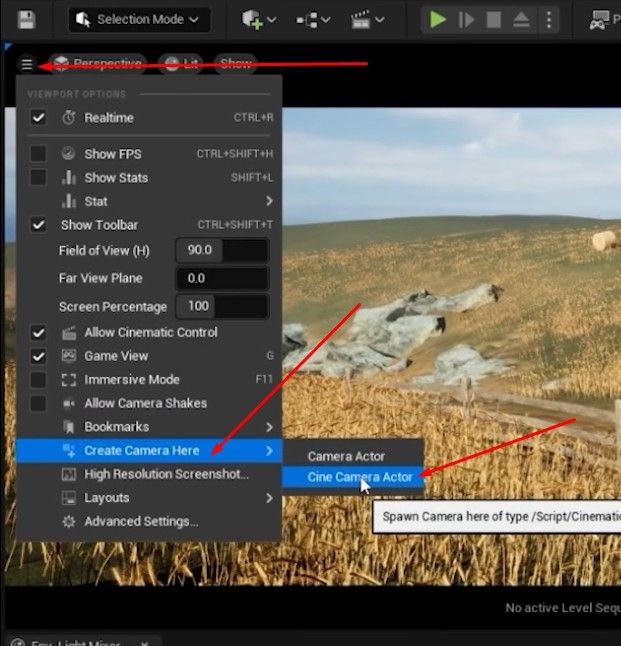
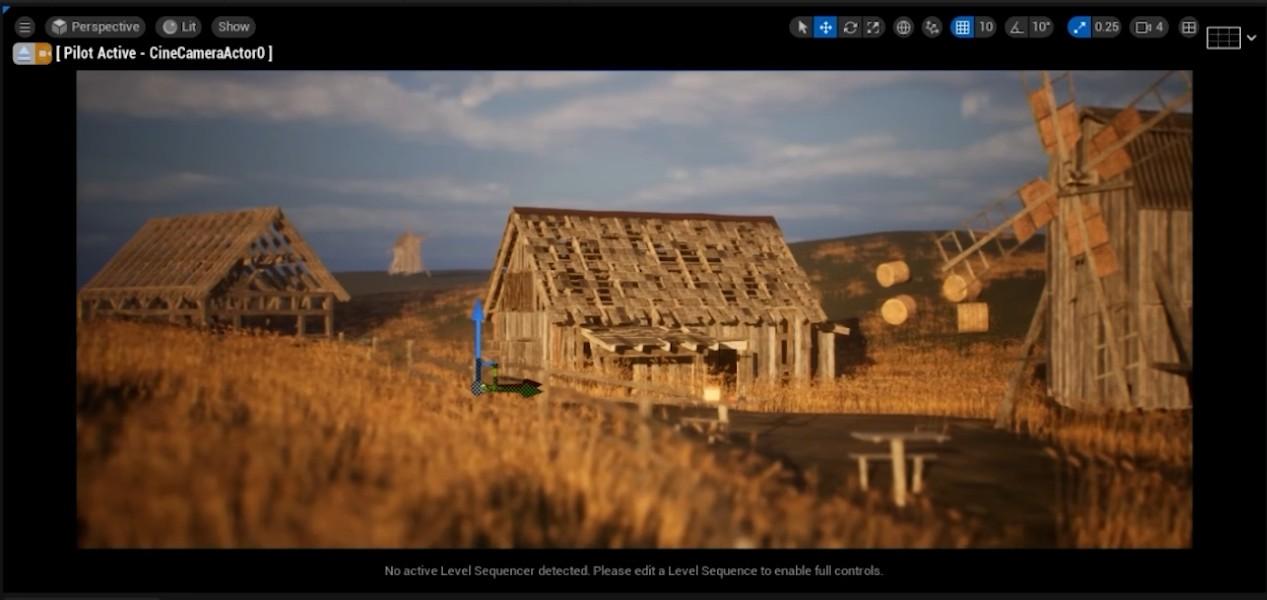
- Add Camera Actor: Place a Cinematic Camera Actor into the scene.
- Pilot the Camera: Right-click the camera and choose “Pilot Camera” to adjust its position and angle for optimal rendering.
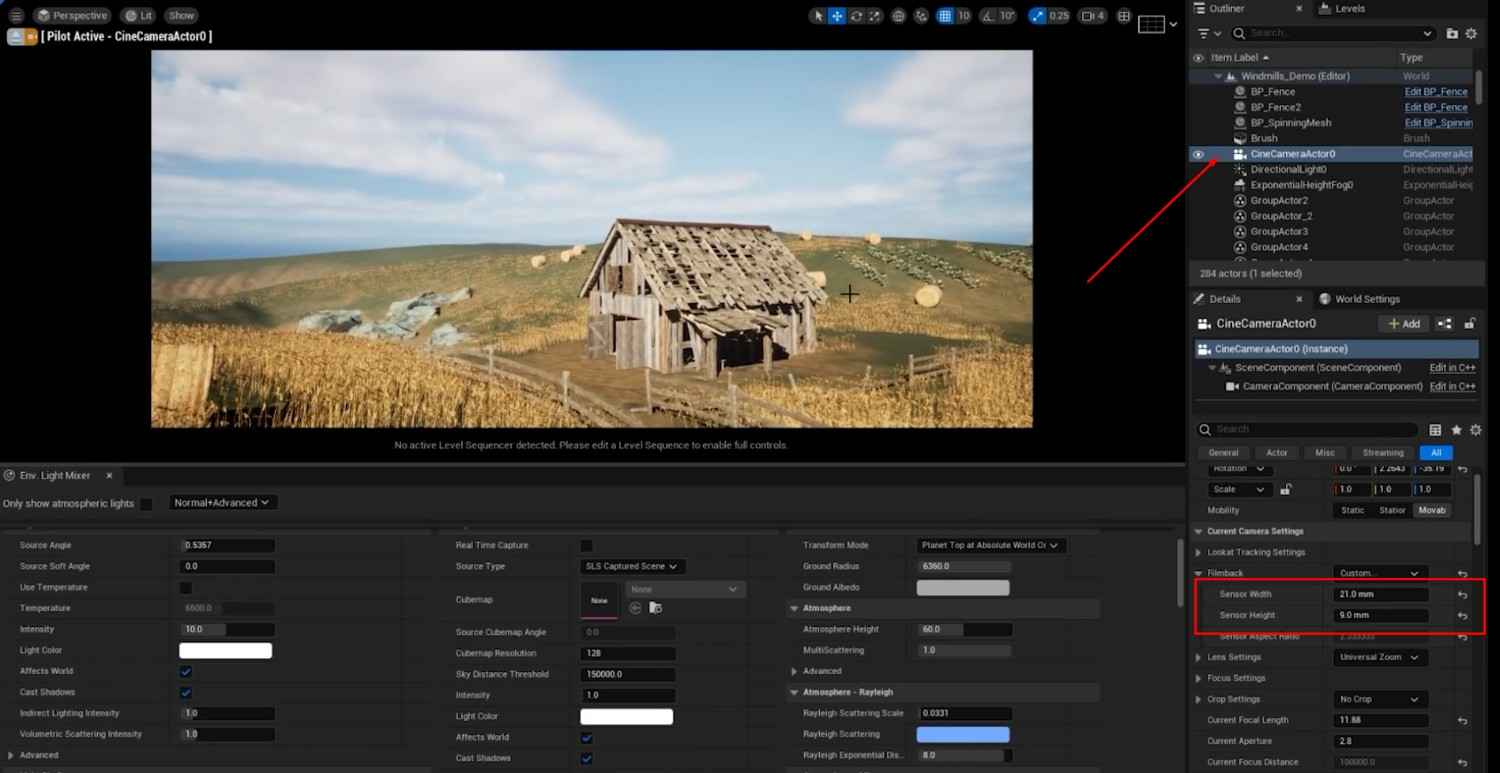
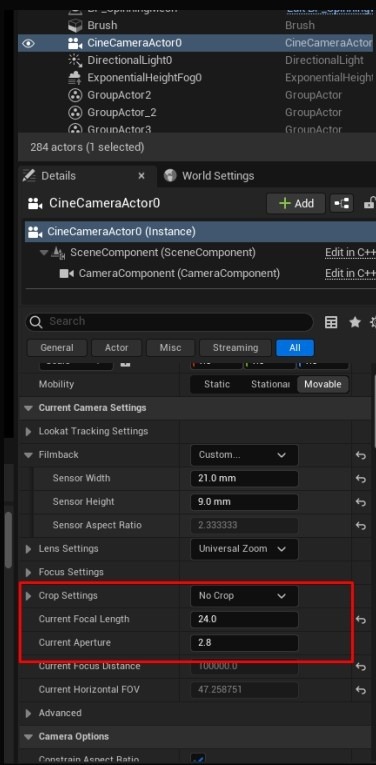
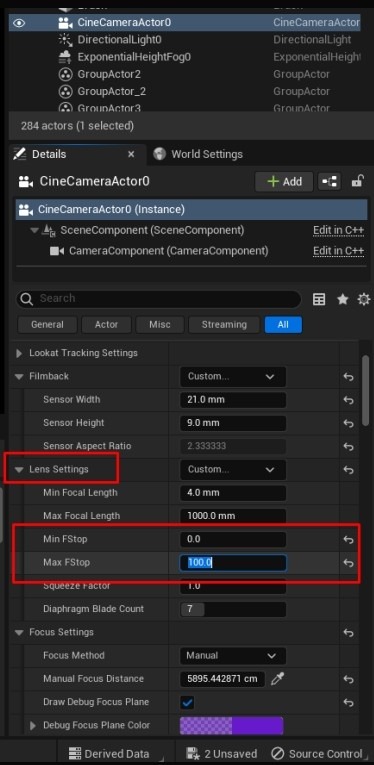
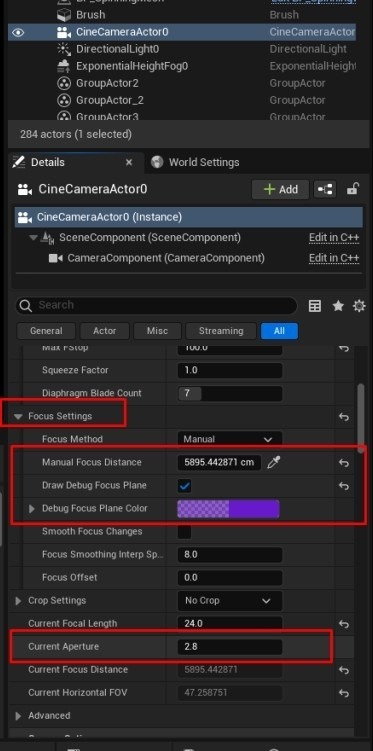
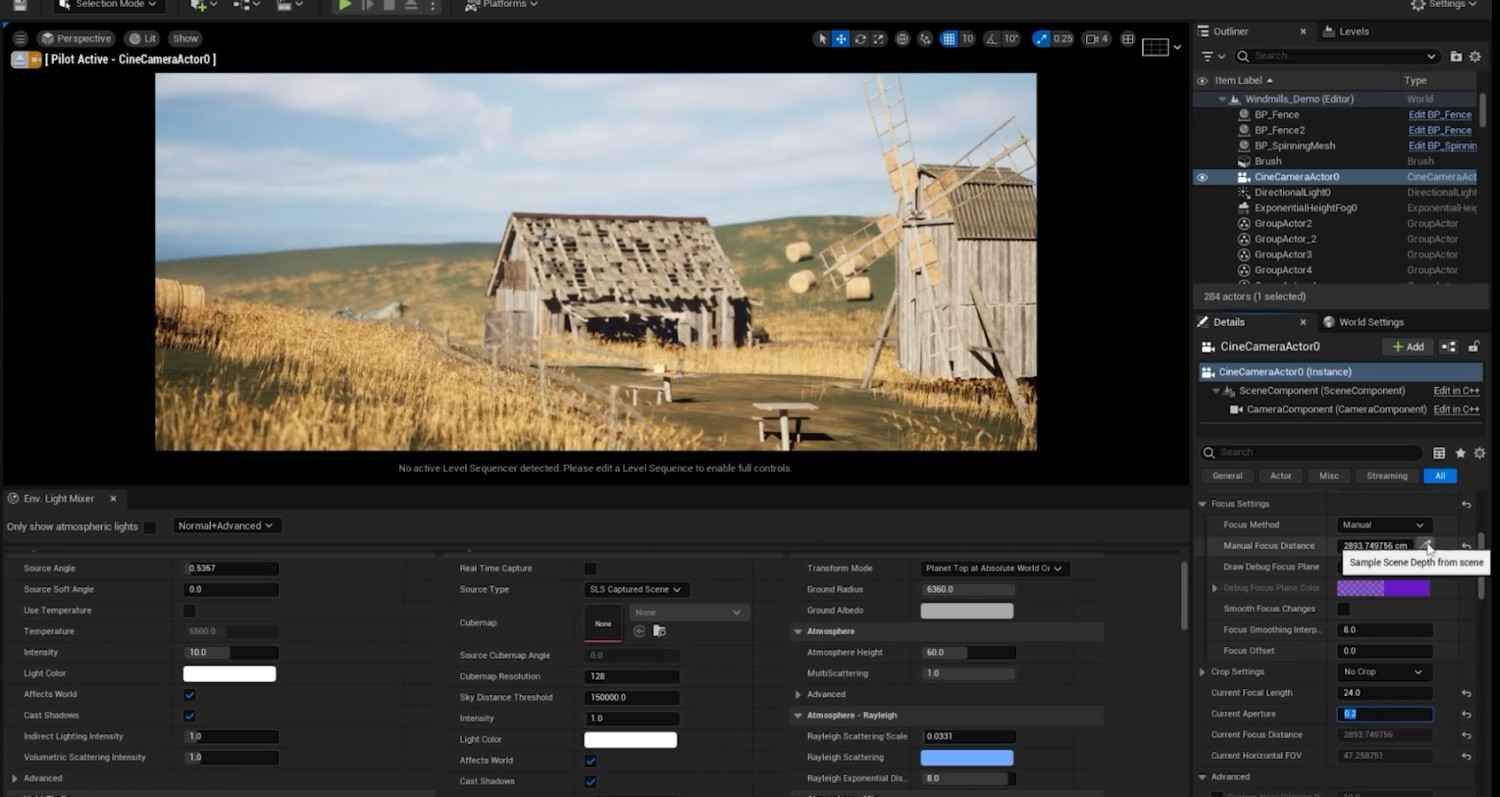
Adjust Camera Settings: Configure the Sensor Width, Height, Crop Settings, Lens Settings, and Focus Settings. Use the Aperture to create background blur while keeping the foreground clear.
6. Fine-Tune Lighting and Composition
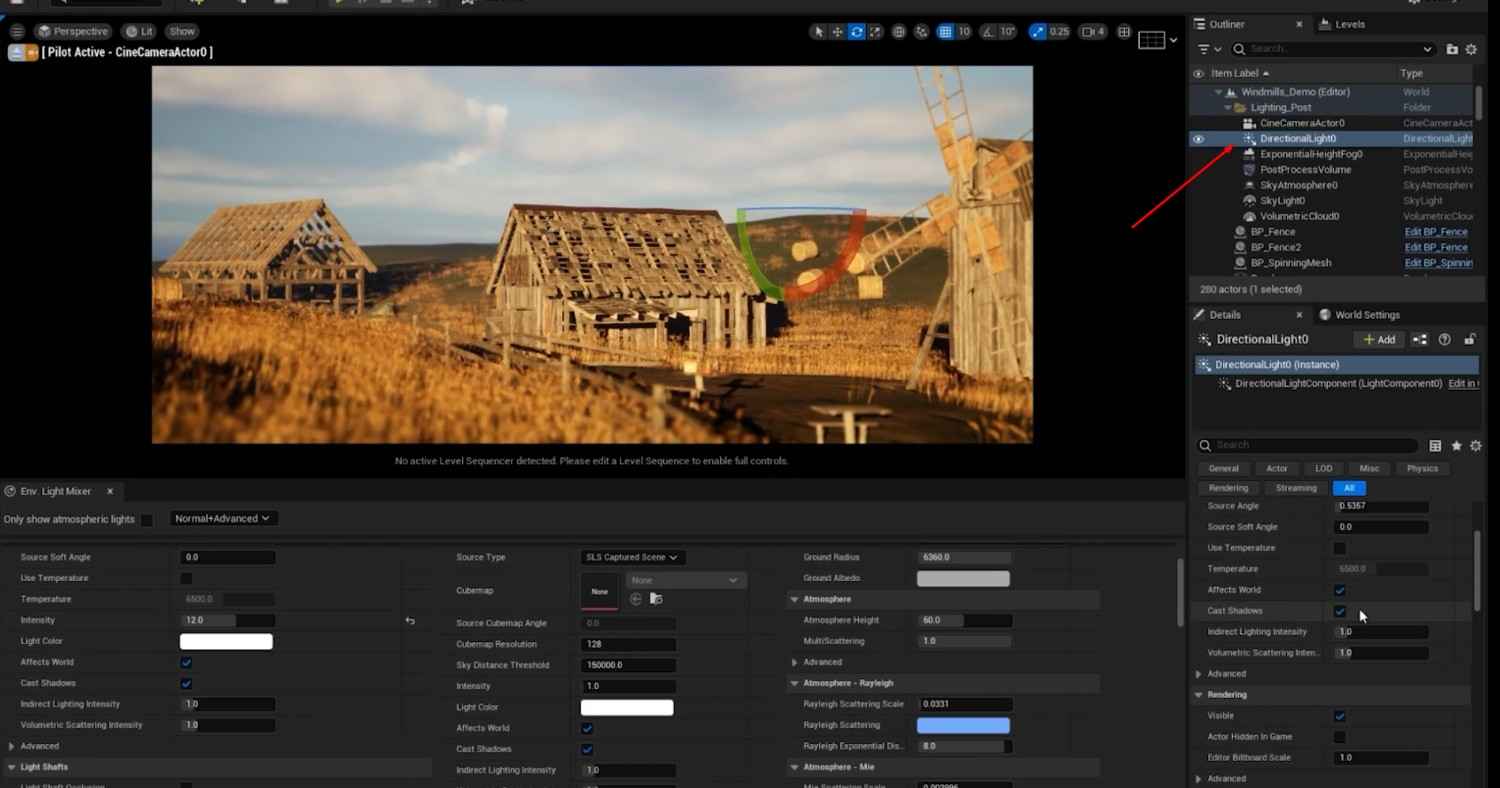
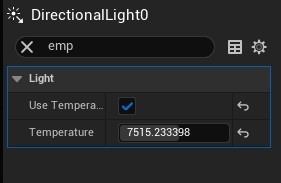
- Adjust Directional Light: Rotate the Directional Light to simulate different times of day. If the pivot is not visible, hold Alt and click with the Middle Mouse Button to reveal it.
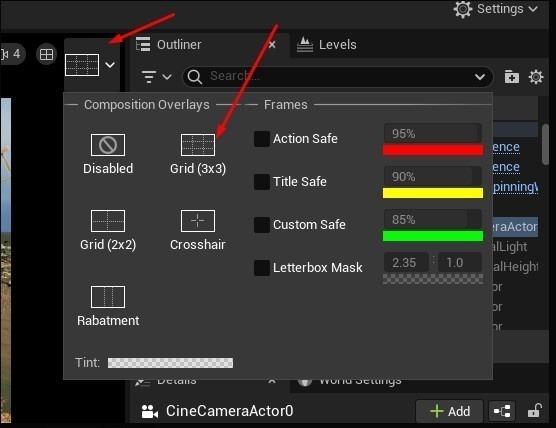
- Add Composition Grid: Apply the Composition Grid to the camera to improve your scene’s framing. Ensure key elements are centered in the grid and the top area is relatively empty.
7. Refine Lighting and Effects
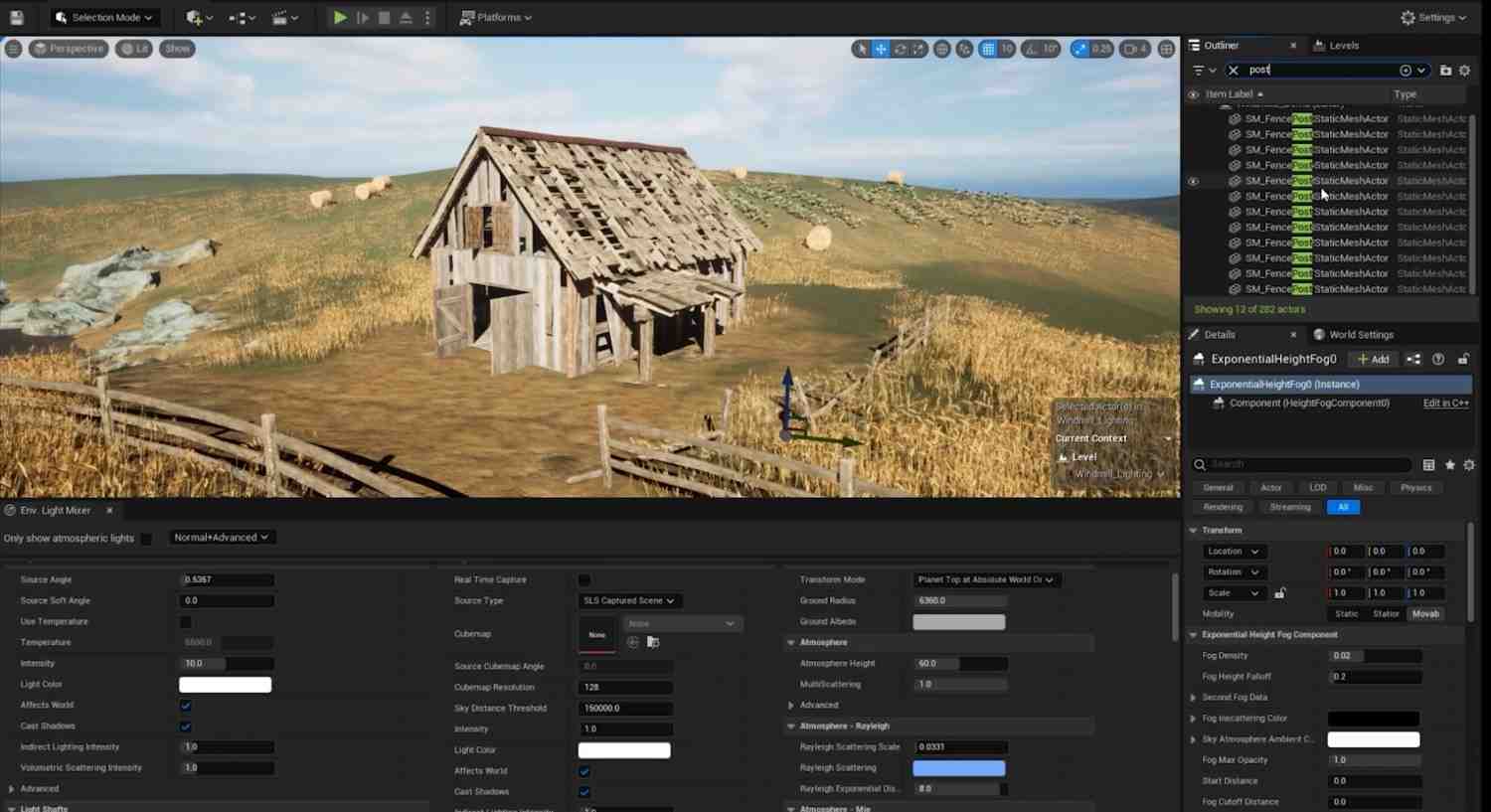
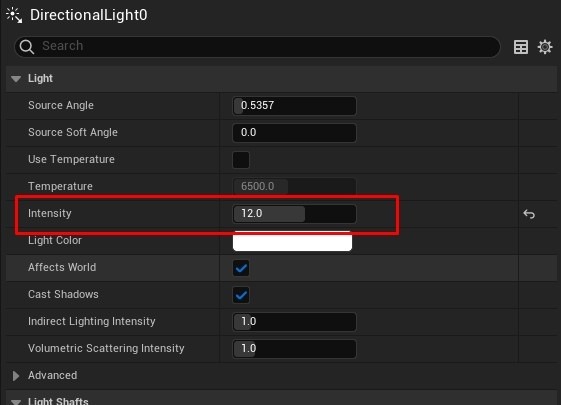
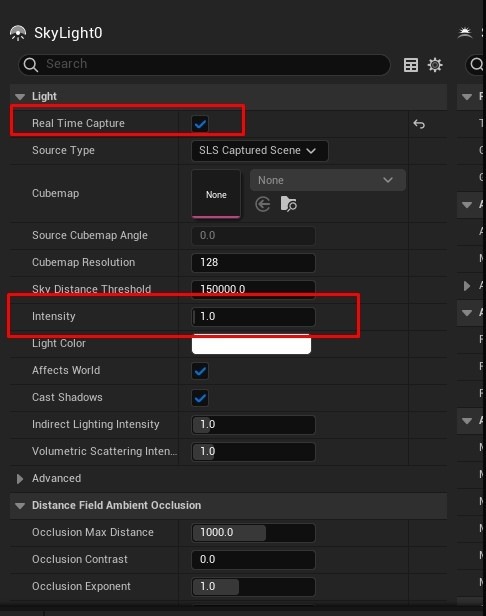
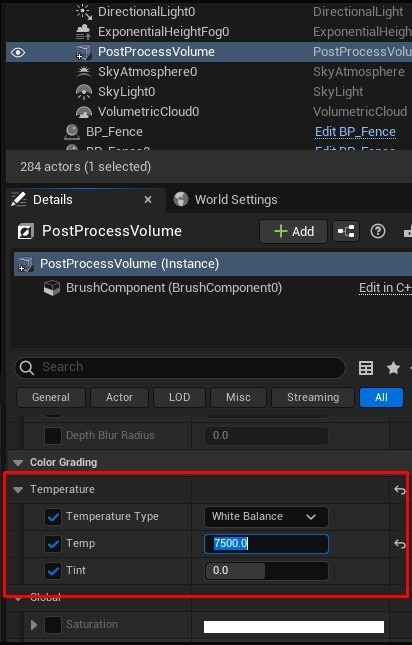
- Control Light Intensity and Temperature: In the Environment Light Mixer, adjust the Intensity of the Directional Light and modify the color temperature to achieve warmer or cooler tones. Enable Real-Time Capture in the Skylight and adjust cloud settings to your preference.
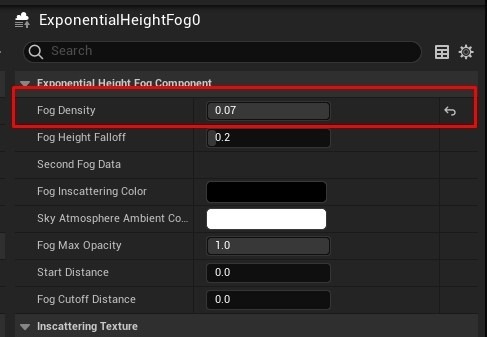
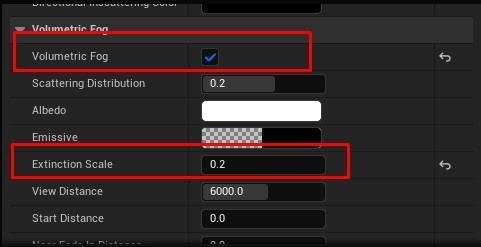
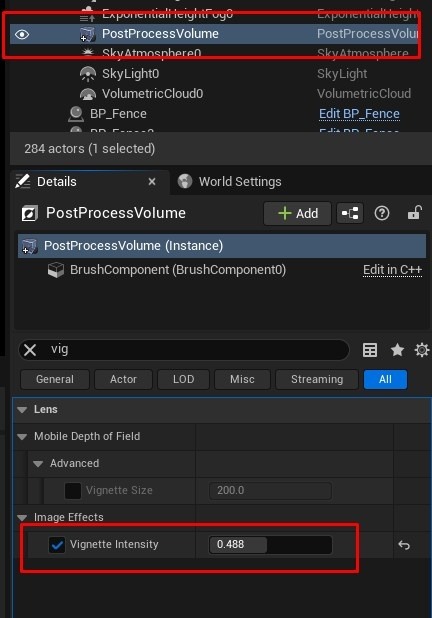
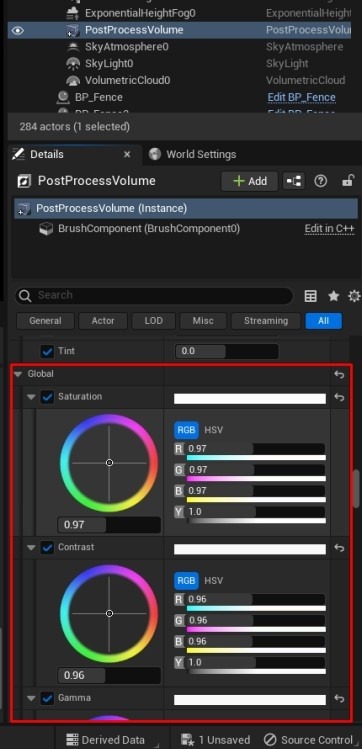
- Adjust Fog and Bloom: Manage fog density, volume, and scale. Add a Bloom effect and enable Vignette in the PostProcessVolume. Fine-tune global colors, contrast, saturation, and gamma as needed.
8. Optimize Camera-Specific Settings
- Camera-Specific Adjustments: Changes in the PostProcessVolume will affect the entire scene, while adjustments in the Cinematic Camera settings impact only the camera view. Make sure to apply changes accordingly.
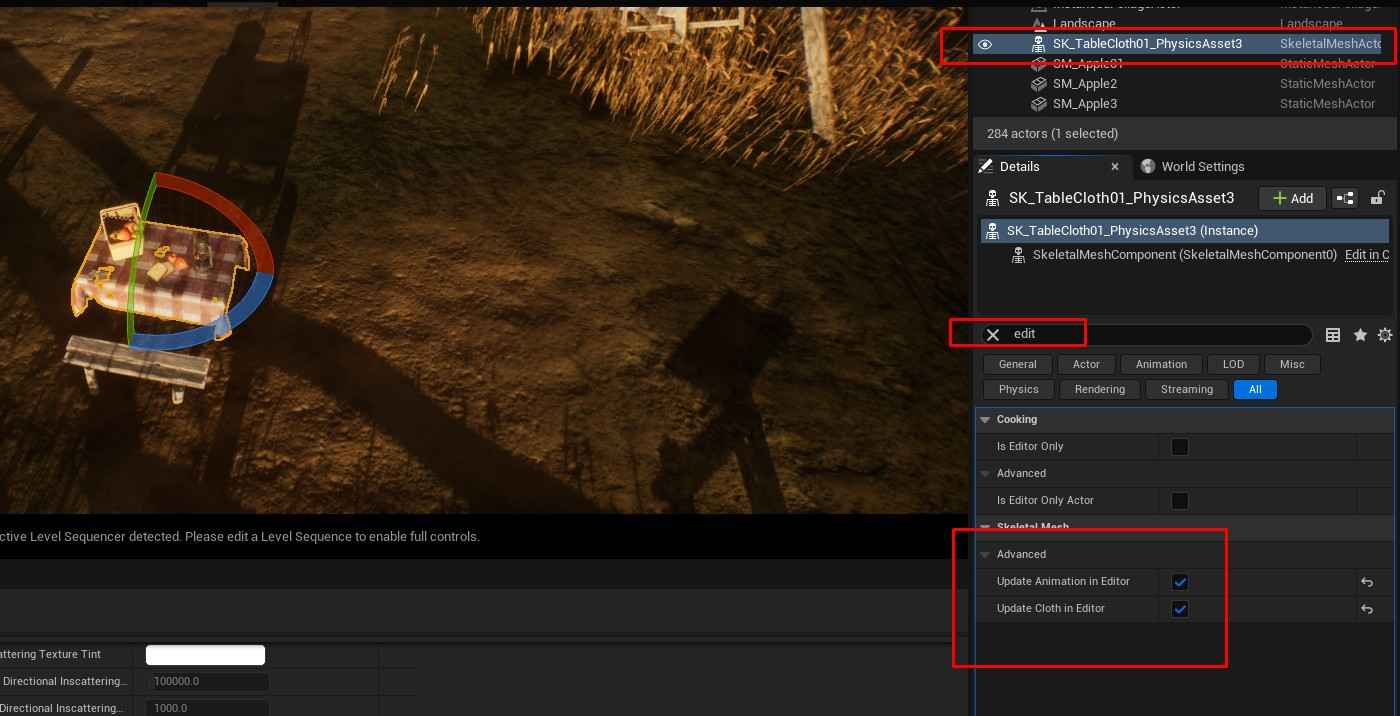
9. Animate Cloth for Realism
- Enable Cloth Animation: Select SK_TableCloth and enable Update Animation in Editor and Update Cloth in Editor in the Details panel to prevent the cloth from appearing flat and enhance realism.
10. Capture and Save Your Render
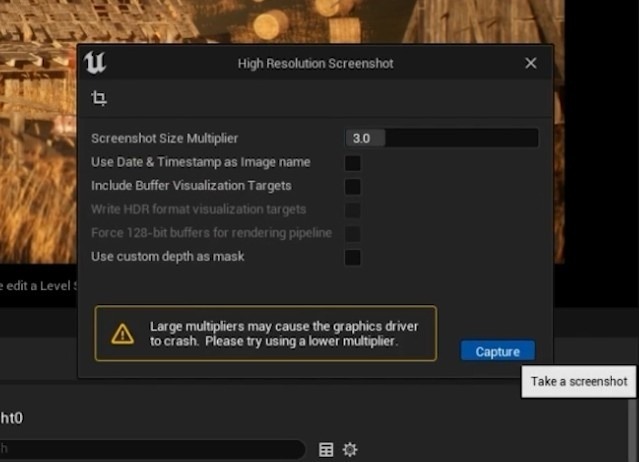
- Take High-Resolution Screenshot: Set the Screenshot Size Multiplier and click Create to capture a high-resolution image of your scene.
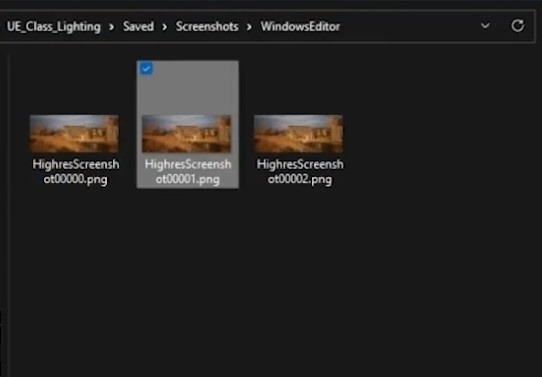
- Locate the Screenshot: Find the saved screenshot in the Screenshot folder within your Unreal project directory.
By following these steps, you’ll effectively set up and refine the lighting in your Unreal Engine environment, resulting in a polished and visually engaging scene.
Conclusion
In closing, if you love creating beautiful environments in Unreal Engine, there are tons of resources available to help you out. Check out our academy programs for deep curriculums designed for people like you who want to get into professional game development: They’re great whether newbies or pros looking to sharpen particular skills.
You can also visit our courses section if you need concrete software learning.
Speaking of which: Industry professionals already doing their thing will also want to attend our exclusive events.
These offer tips from seasoned pros that might just take your work up a notch (or five)—plus insights on advanced techniques for those further along their creative path.
Details about how to apply and whether financial aid is possible can be found under Enrolment & Funding. So don’t put it off any longer: If turning what you love into a job seems doable with some support from others who have been there too (and succeeded), then check the eligibility criteria now! Apply immediately!!